Description
Adult Sinusitis
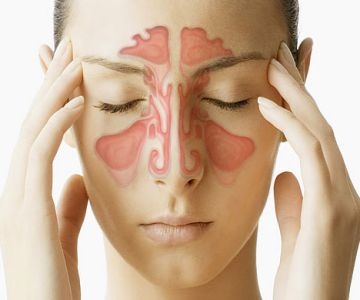
Sinusitis refers to infection, inflammation, or swelling of the sinuses and nasal cavity. The sinuses are a group of hollow spaces that surround the nose and eyes. Sinus infections include cloudy or colored discharge from the nose with nasal blockage or facial pain/pressure. Other symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, lack of or reduced sense of smell, dental pain, and ear fullness. The symptoms can be serious enough to disturb your quality of life or general well-being.
Sinus infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi. A viral sinus infection has similar symptoms as bacterial infections, but improves within 10 days and does not get worse. A bacterial sinus infection is defined by how long the symptoms last. The three types are acute (short course), recurrent (repeated), or chronic (long lasting). An acute bacterial sinus infection is one that either fails to get better within 10 days or has suddenly gotten worse after an initial period of getting better. Acute bacterial sinus infection lasts less than four weeks. Recurrent bacterial sinus infections are when an acute sinus infection occurs four or more times in a one-year period. A chronic sinus infection is when two or more symptoms and swelling lasts for 12 weeks or longer.
A fungal sinus infection is one that is linked with chronic symptoms. Fungal sinus infections usually occur with people who have weak immune systems. Fungal sinus infections can also occur with people who have used long-term antibiotics.
What causes adult sinusitis?
A sinus infection is typically caused by a viral upper respiratory infection, like a cold. A viral infection does not get better from taking antibiotics. Acute bacterial sinus infections are caused by a bacterial infection.
What can you do?
You should see a healthcare provider soon after symptoms occur. Early diagnosis may help avoid misdiagnosis or delayed treatment and worse results. There are several types of sinus infections, so it is important to get the correct diagnosis for proper treatment. Treatment options should be discussed with the healthcare provider after diagnosis. Antibiotics do not work for viral sinus infections. Antibiotics are not recommended for all types of bacterial infections.
How is adult sinusitis diagnosed?
Your ENT doctor can diagnose a sinus infection by reviewing the medical history and doing a physical exam. The healthcare provider should identify acute bacterial sinus infection from viral sinus infection or noninfectious conditions. Your healthcare provider should diagnose an acute bacterial sinus infection will be diagnosed when:
- Symptoms (facial pain-pressure-fullness, nasal blockage) or signs (cloudy or colored nasal drainage) or both continue without getting better for at least 10 days after the onset of upper respiratory symptoms like a cold or,
- Symptoms or signs of a sinus infection worsen within 10 days after getting better (double worsening).
Other conditions can seem like a sinus infection. For instance, a headache alone may not mean a sinus infection. With a sinus infection there is usually cloudy or colored nose drainage.
An acute sinus infection is diagnosed when there are up to four weeks of colored or cloudy runny nose with nasal blockage, facial pain-pressure-fullness, or both. A healthcare provider should decide between chronic and recurrent acute sinus infections from single incident of acute bacterial sinus infections and other causes of sinonasal (nose and sinus) symptoms.
The ENT doctor cannot diagnose chronic sinus infection based on symptoms alone. He will also need to see nasal swelling or inflammation on exam. The healthcare provider may use tools such as an endoscope. These types of tools can offer a better view of your sinuses. The healthcare provider may also order a CT (CAT) scan to view sinonasal swelling.
The CT scan may confirm a diagnosis of chronic sinus infections. For chronic sinus infections, the healthcare provider should confirm whether nasal polyps are present. Nasal polyps are harmless growths. Having nasal polyps will modify care of your symptoms.
Instead of prescribing antibiotics right away for your acute bacterial sinus infection, your healthcare provider may suggest a treatment option known as watchful waiting. This option usually includes a seven-day waiting period without antibiotics to see if you get better on your own.
How is adult sinusitis diagnosed?
It is important to properly diagnose viral and bacterial sinus infections. If you have heart, kidney or liver diseases, your ENT doctor may consider different treatment.
For a viral sinus infection: Talking with your ENT doctor can help you make decisions about the treatment of symptoms.
For an acute bacterial sinus infection: Your ENT doctor should offer either watchful waiting without antibiotics or an antibiotic.
For a chronic sinus infection: Your healthcare provider may recommend saline nasal rinse or topical intranasal corticosteroids.
Do I need surgery for my sinusitis?
Surgery for the sinuses is done when the symptoms can’t be controlled with medications and other treatments. The most common type of surgery for the sinuses is called endoscopic sinus surgery, because pencil-sized scope (“endoscope”) is used to see inside the nose and sinuses and guide the surgery.
Medications that are delivered to the surface of nose and sinuses, like sprays and irrigations, can get into the sinuses better after surgery as well.

